- Abstract Expressionism
- Art Deco
- Art Nouveau
- Avant-Garde
- Baroque.
- Bauhaus
- Classicism
- CoBrA
- Color Field Painting
- Conceptual Art
- Constructivism
- Cubism
- Dada / Dadaism
- Digital Art
- Expressionism
- Fauvism
- Futurism
- Geometric
- Harlem Renaissance
- Impressionism
- Installation Art
- Minimalism
- Naturalism
- Neo-Impressionism
- Neoclassicism
- Neon Art
- Op Art
- Performance Art
- Photorealism
- Pop Art
- Portraiture
- Post-Impressionism
- Precisionism
- Rococo
- Romanticism
- Spiritual Art
- Street Art
- Surrealism
- Suprematism
- Symbolism
- Zero Group
- What is an Art Style?
- 1.How Many styles of art are there?
- 2.What are the examples of 19th century art styles?
- 3.What are the examples of 1940s art style?
- 4.What are the examples of 1950s art style?
- 5.What are examples of 1960's art style?
- 6.What are the examples of cool art styles?
- 7.What are the examples of unique art styles?
- 8.What are the examples of easy art styles?
- 9.What are the examples of simple cute art styles?
- 10.What are the examples of old art styles?
- 11.What are the examples of classical art styles?
- 12.What are the examples of historical art styles?
- 13.What are the examples of colorful art styles?
- 14.What are the examples of drawing styles?
- 15.What are the examples of aesthetic art styles?
- 16.What are the types of painting styles?
- 17.What is an Artistic Movement?
- 18.What is an art period?
- 19.What are the types of fine arts?
- 20.What are the different types of artists?
- 21.What are the different types of art schools?
- 22.What are the names of the most common methodologies of art?
- 23.What are the various forms of art?
- 1.
"Art" is simply human creations that express ideas, emotions, or beauty. Art uses different mediums and techniques to evoke experiences, challenge perceptions, or simply delight the senses of the viewers.
There are different forms of art. For example, visual arts, performing arts, and literary arts. Every art movement expresses ideas and emotions.
This is where the various art styles stem from. The desire to express ideas in a unique way has led to more than 50 types of art movements.
The types of art include various art styles and art movements such as Abstract Expressionism, Art Deco, Art Nouveau, Avant-garde, Baroque, Bauhaus, Classicism, CoBrA, Color Field Painting, Conceptual Art, Constructivism, Cubism, Dada / Dadaism, Digital Art, Expressionism, Fauvism, Futurism, Geometric, Harlem Renaissance, Impressionism, Installation Art, Minimalism, Naturalism, Neo-Impressionism, Neoclassicism, Neon Art, Op Art, Performance Art, Photorealism, Pop Art, Post-Impressionism, Precisionism, Rococo, Romanticism, Spiritual Art, Street Art, Surrealism, Suprematism, Symbolism, and Zero Group.
The types of arts, including different artistic styles and artistic movements, are described below:
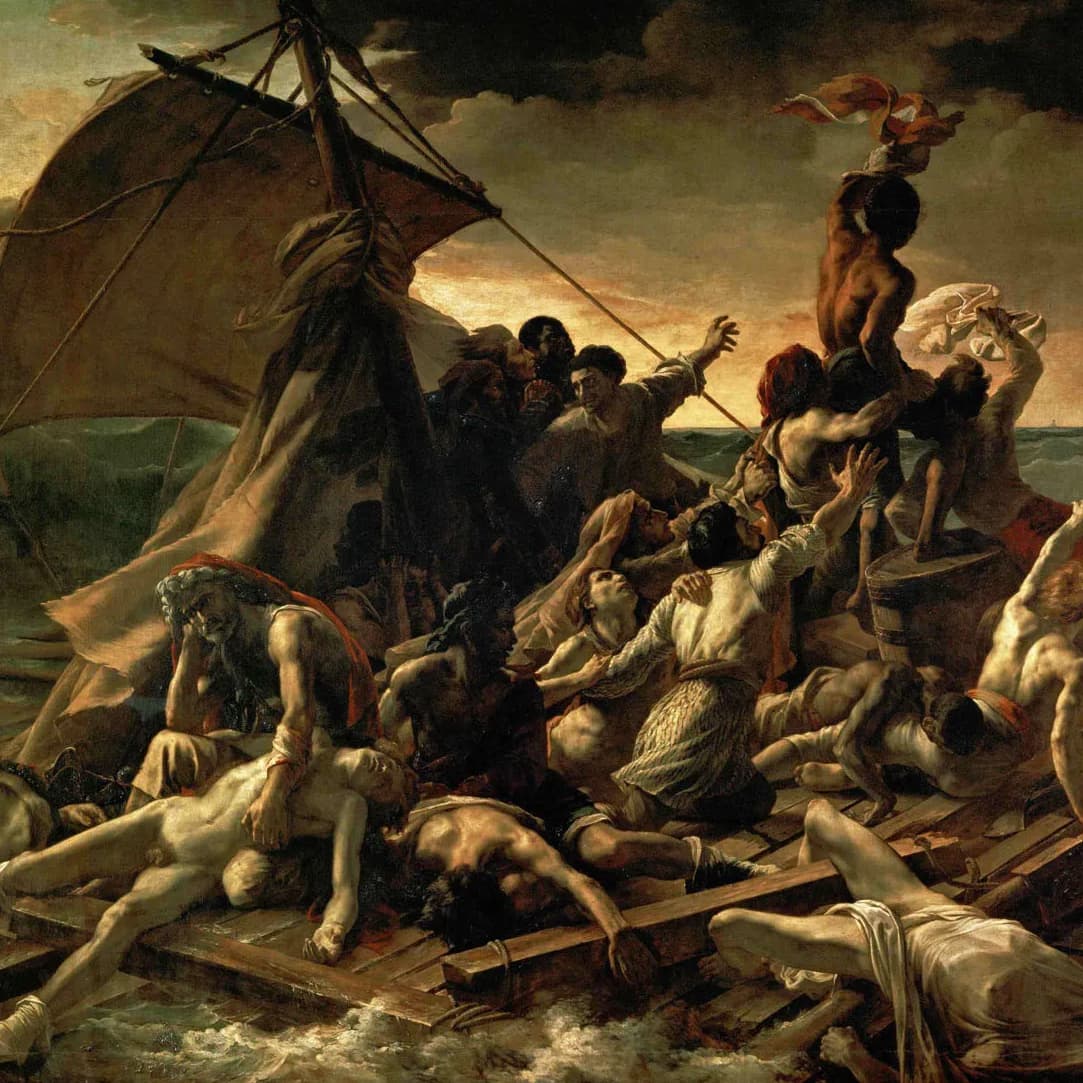
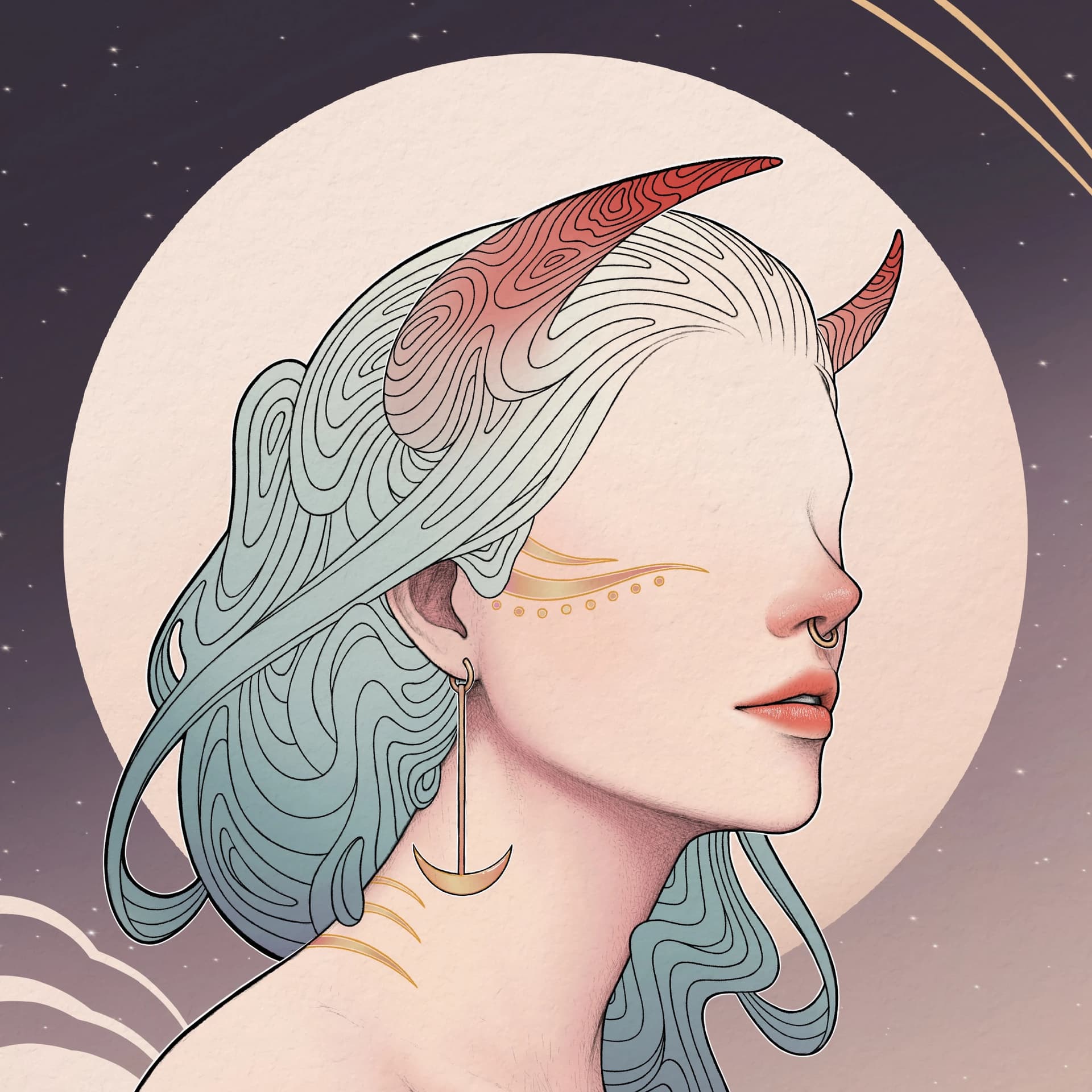








































Abstract Expressionism

Abstract expressionism started in the late 1940s in the United States. This art movement was influenced by post-WWII American artists like Jackson Pollock and Mark Rothko. Some popular art styles include One: Number 31 by Jackson Pollock, Rothko Chapel paintings by Mark Rothko, and Woman I by Willem de Kooning.
Read more about Abstract Expressionism.
Art Deco

This artistic movement is a mix of modernity and luxury. It combines geometric forms, rich colors, and lavish materials to evoke a sense of glamor, progress, and opulence.
Art Deco emerged in the early 1910s and flourished during the 1920s and 1930s. It drew inspiration from various types of art styles like the Early 20th Century Modernism, Cubism, Art Nouveau, and The Machine Age.
Some infamous art style paintings from Art Deco include Autoportrait by Tamara de Lempicka, American Progress by Jose Maria Sert, and Victoire by René Lalique.
Read more about Art Deco.
Art Nouveau
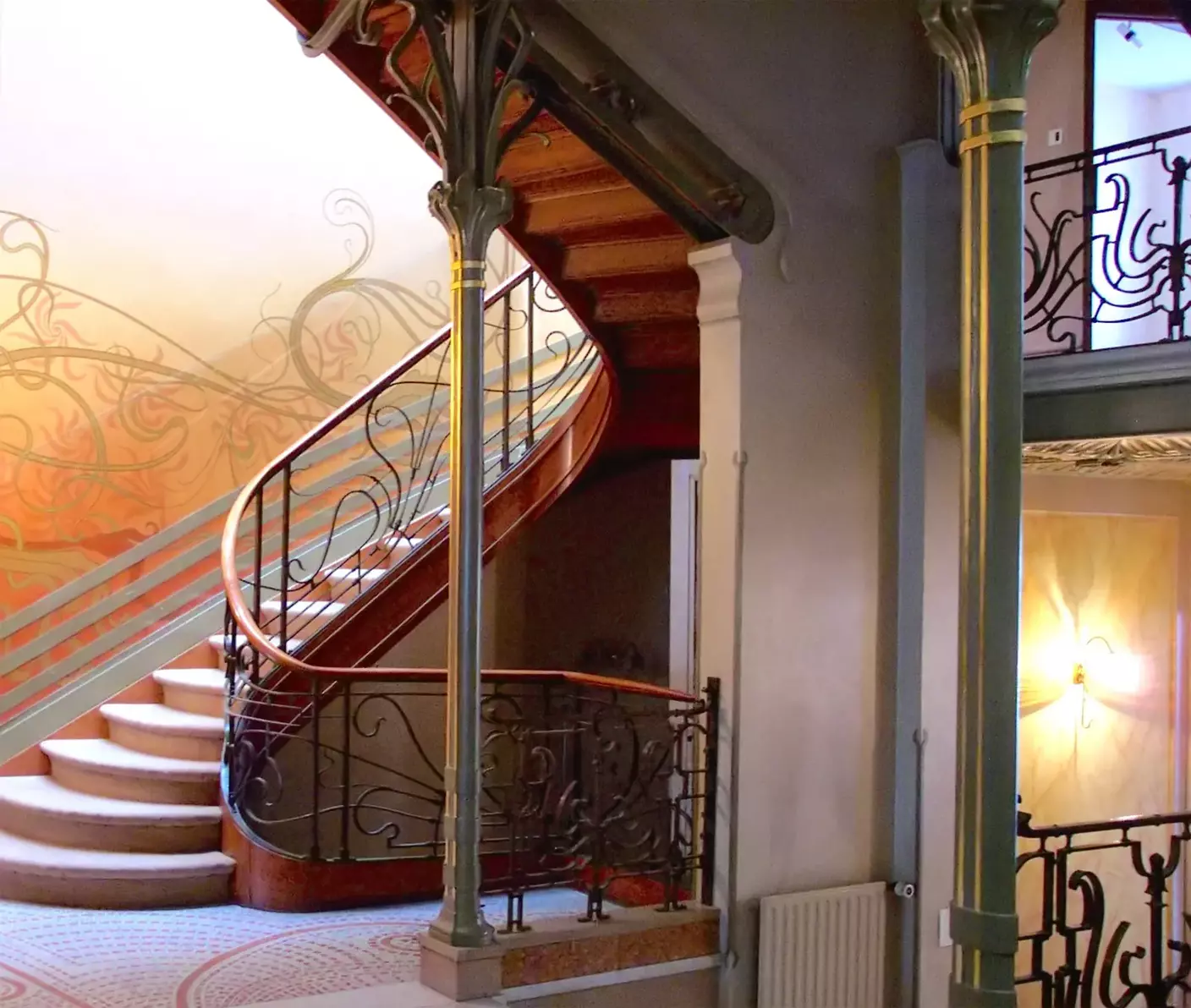

Similar to Art Deco, this art movement didn’t result from a single source of inspiration. It was a confluence of artistic movements in the late 19th century, such as Japanese Art (Ukiyo-e), Romanticism, and Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood. The Kiss by Gustav Klimt, Primavera by Sandro Botticelli, and Casa Batlló by Antoni Gaudí are famous art styles from this era.
Read more about Art Nouveau.
Avant-Garde

Romanticism, Industrial Revolution, Social and Political Upheavals, and Philosophical Movements influenced its beginning. Some of the most famous Avant-Garde paintings incude Les Demoiselles d'Avignon by Pablo Picasso, Guernica by Pablo Picasso, and Fountain by Marcel Duchamp.
Read more about Avant-Garde.
Baroque.
Baroque art movement refers to grandiose compositions, dramatic lighting, and religious themes.
The term "Baroque" originated from the Medieval Latin word "baroco," used to describe a complex and flawed argument. This art style emerged in the late 16th century in Italy.

Its beginning was influenced by a mix of historical and artistic factors like Counter-Reformation, Renaissance Legacy, and Theatrical Influence. Popular types of art from Baroque include The Ecstasy of Saint Teresa by Gian Lorenzo Bernini, Las Meninas by Diego, and David by Michelangelo.
Read more about Baroque.
Bauhaus
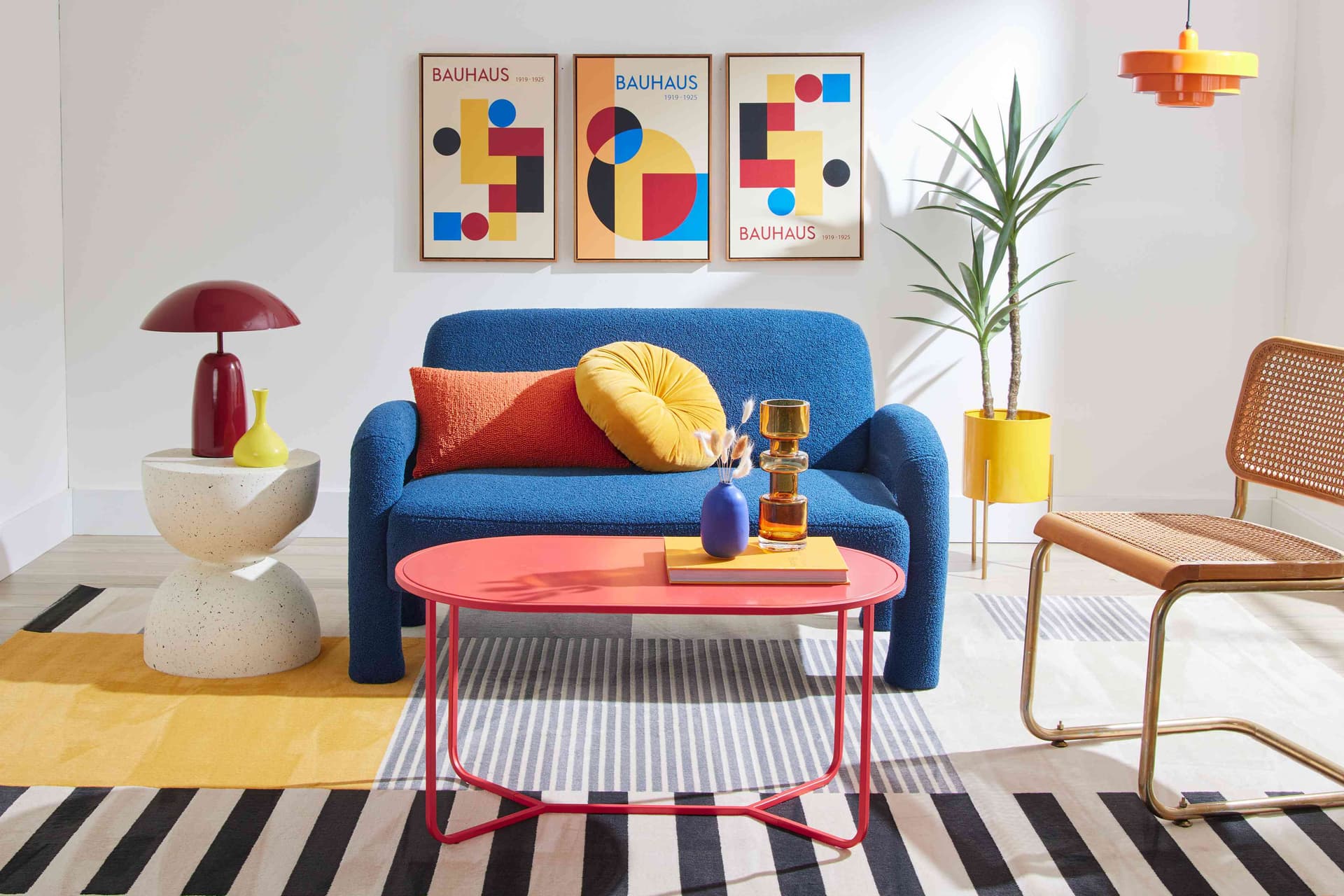

The term has German origin wherein Bau translates to building, and Haus translates to house. So, it literally means "building a house." The Bauhaus movement was influenced by De Stijl, The Machine Age, and Mr. Walter Gropius. The famous paintings that we all know today as Gropius House, Universal typeface, and Posters, originated during the Bauhaus.
Read more about Bauhaus.
Classicism

Classicism is primarily a movement of the 17th, 18th, and early 19th centuries. The rediscovery of ancient Greek and Roman texts laid the groundwork for its beginning. Popular artistic styles from Classicism include The Death of Marat by Jacques-Louis David, The Oath of the Horatii by Jacques-Louis David and Venus de Milo.
Read more about Classicism.
CoBrA
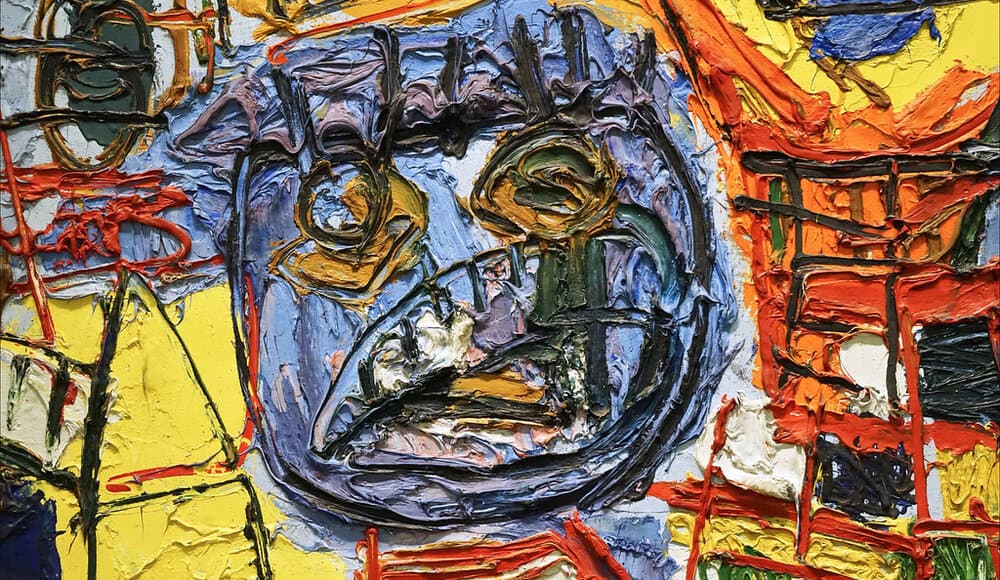

This art movement officially began in 1948 and disbanded around 1951. Its key influences were Surrealism, Primitive Art, and Existentialism. Notable works include Questioning Children by Asger Jorn, Composition by Karel Appel, and Fête Nocturne by Corneille.
Read more about CoBrA.
Color Field Painting

Mark Rothko's early use of large, color-saturated rectangles on canvas is often seen as a pivotal moment in its development. Some popular Color Field Paintings include No. 61 & Seagram Mural, PH-147 & 1957-P, and After Hours.
Read more about Color Field Painting.
Conceptual Art
Conceptual Art movement uses everyday objects, actions, or performances to convey a message or spark a reaction. This art movement emerged in the mid-20th century.

Its beginning can be traced back to Henry Flynt and Sol LeWitt. Henry Flynt coined the term "concept art", describing it as art where the concept takes priority over traditional artistic skills. Sol LeWitt also published a paragraph defining conceptual art in 1967. The Fountain, One and Three Chairs, and I ♥ NY are famous conceptual art styles paintings.
Read more about Conceptual Art.
Constructivism

Sculptors Antoine Pevsner and Naum Gabo, known for their geometric metal sculptures, coined the term "Constructivism" around 1920 in their "Realistic Manifesto." Notable constructivist creators include Vladimir Tatlin, El Lissitzky, Alexander Rodchenko, and Kazimir Malevich.
Read more about Constructivism.
Cubism

Cubism is primarily an art movement of the 20th century. In 1908, a French art critic named Louis Vauxcelles saw a painting by Georges Braque and mockingly referred to it as "bizarreries cubiques," which translates to “bizarre cubes.”
Cubism originated from there. Popular Cubist artworks include Guernica, Violin and Candlestick, and Head of a Woman.
Read more about Cubism.
Dada / Dadaism

In 1916, at the birth of Dada in Cabaret Voltaire, a dictionary was opened at random, and "Dada" (meaning "hobby-horse" in French) was chosen, embodying the movement's nonsensical spirit. Ultimately, it became a symbol of the defiance of established meaning. Infamous Dadaism artworks include Fountain (1917), L.H.O.O.Q. (1919), and Merzbild (1919).
Read more about Dadaism.
Digital Art

The rise of Digital Art happened because of Computer Science advancements, Fluxus movement, and a changing cultural landscape. Famous digital art style painting include "The Next Day" by Robbie Barrat, "Allegory of the Cave" by Nancy Bechtol, and "Data Dreams" by Casey Reas and Noah Bre.
Read more about Digital Art.
Expressionism
Expressionism emphasizes emotional expression over realistic depiction. Expression artists use distorted forms, bold colors, and intense brushwork to convey their inner anxieties and psychological experiences. The term "Expressionism" emerged in Germany around the early 1900s when art critic Julius Meier-Graefe used it to describe a group of artists whose work emphasized expression over naturalism.

The rise of Expressionism wasn't due to one person or movement, but a combination of Post-Impressionism, Fauvism, German and Austrian anxieties, Primitive Art, and Psychoanalysis. The Scream (1893), The Kiss (1907-08), and Sorrow (1910) are popular expressionist paintings.
Read more about Expressionism.
Fauvism

The term "Fauvism" originated in 1905 when Louis Vauxcelles used the term "les fauves" (meaning "the wild beasts") to describe the radical works exhibited by Henri Matisse.
Henri Matisse and Paul Gauguin are the leaders of Fauvism. Matisse's bold use of color and Gauguin's paintings from Tahiti influenced other Fauvism artists.
Famous works include Dance (I) (1909), Bathers at Collioure (1905), and Port of Lorient (1905).
Read more about Fauvism.
Futurism
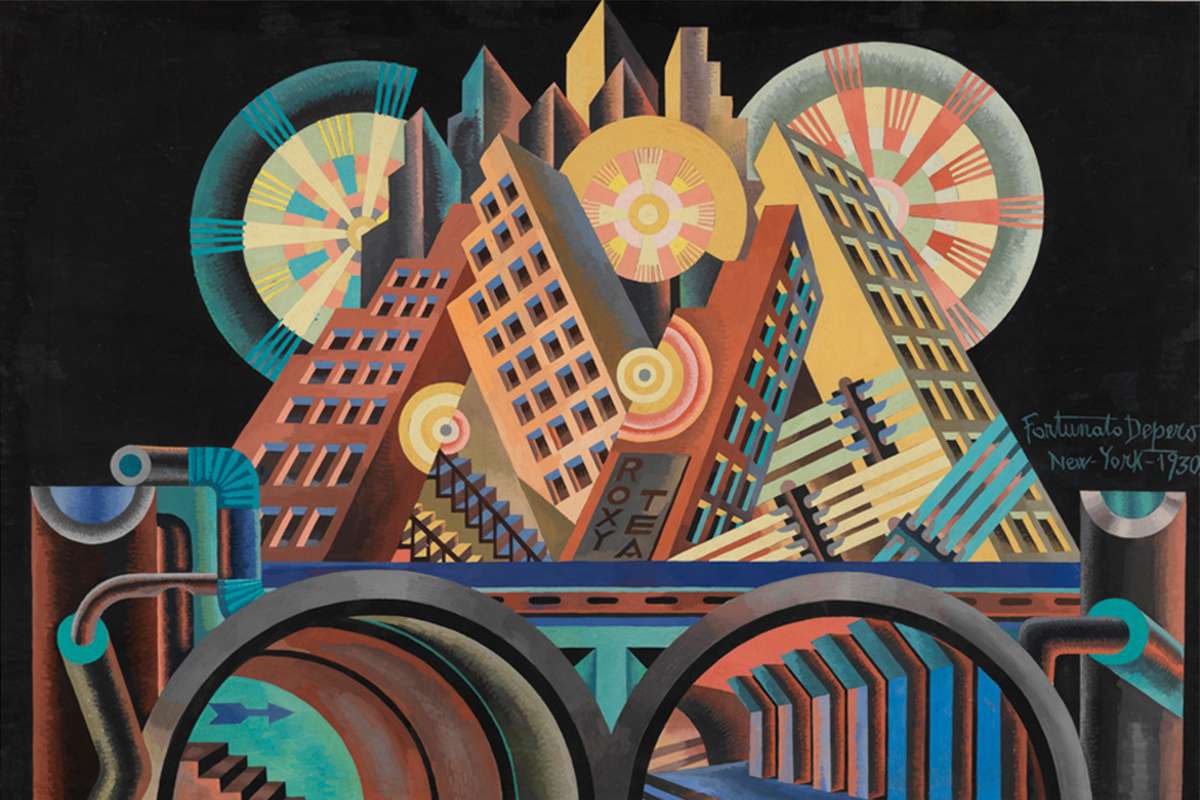

The term "Futurism" was coined in 1909 by Italian poet Filippo Tommaso Marinetti, who published the "Manifesto del Futurismo". "Futurismo" translates directly to Futurism in English. So, it's primarily an art movement of the 20th century.
Popular works in Futurism art include Dynamism of a Dog on a Leash by Giacomo Balla, Red Slippers by Constantin Brâncuși, and Armored Train in Action by Gino Severini.
Read more about Futurism.
Geometric

The origin of the term is a bit hazy, but it likely emerged in the early 20th century. It is inspired by multiple factors, including Egyptian Art, Greek Vase Painting, Islamic Art, Non-Western Art, and Artistic traditions from Africa, the Americas, and Oceania. The Step Pyramid of Djoser is the most famous geometric artwork.
Read more about Geometric art.
Harlem Renaissance

Artists use a variety of media, including painting, sculpture, photography, and textiles, depicting everyday life, historical events, and social justice issues. It started around 1918 and waned during the Great Depression (1929-1939)
The Harlem Renaissance was sparked by the mass movement of African Americans from the rural South to urban centers like Harlem in New York City. Notable artists include Aaron Douglas, Roy DeCarava, and Alma Thomas.
Read more about Harlem Reneissance.
Impressionism
Impressionism refers to capturing fleeting effects of light and atmosphere. Artists use loose brushstrokes, vibrant colors, and everyday subject matter to create a sense of immediacy and impression. In 1874, a French art critic named Louis Leroy used the term "Impressionism" in a mocking review of the first exhibition by impressionist artists.

Consequently, impressionism emerged as a distinct movement in the late 19th century. Notable works are Water Lilies by Claude Monet, Luncheon on the Grass by Édouard Manet, and A Sunday Afternoon on the Island of La Grande Jatte by Georges Seurat.
Read more about Impressionism.
Installation Art

It started during the mid-20th century when artists began creating site-specific works that interacted with the surrounding environment. These works challenged the limitations of the gallery space. Anish Kapoor, Olafur Eliasson, Random International, and Carsten Höller are remarkable installation artists.
Read more about Installation Art.
Minimalism

Some minimalist artists found inspiration in Zen aesthetics, which emphasizes simplicity, clean lines, and a focus on the present moment. You can see this in Specific Object by Donald Judd, Untitled by Carl Andre, Firelight by Dan Flavin, and Breath by Eva Hesse.
Read more about Minimalism.
Naturalism

French painter Gustave Courbet is considered important in the early stages of Naturalism. His work, like "A Burial at Ornans," depicted everyday people with a stark realism that challenged the idealized portrayals in academic art. His other famous paintings include The Desperate Man, Studio of the Painter: A Real Allegory Determining a Seven-Year Phase of My Artistic and Moral Life, and The Deer.
Read more about Naturalism.
Neo-Impressionism
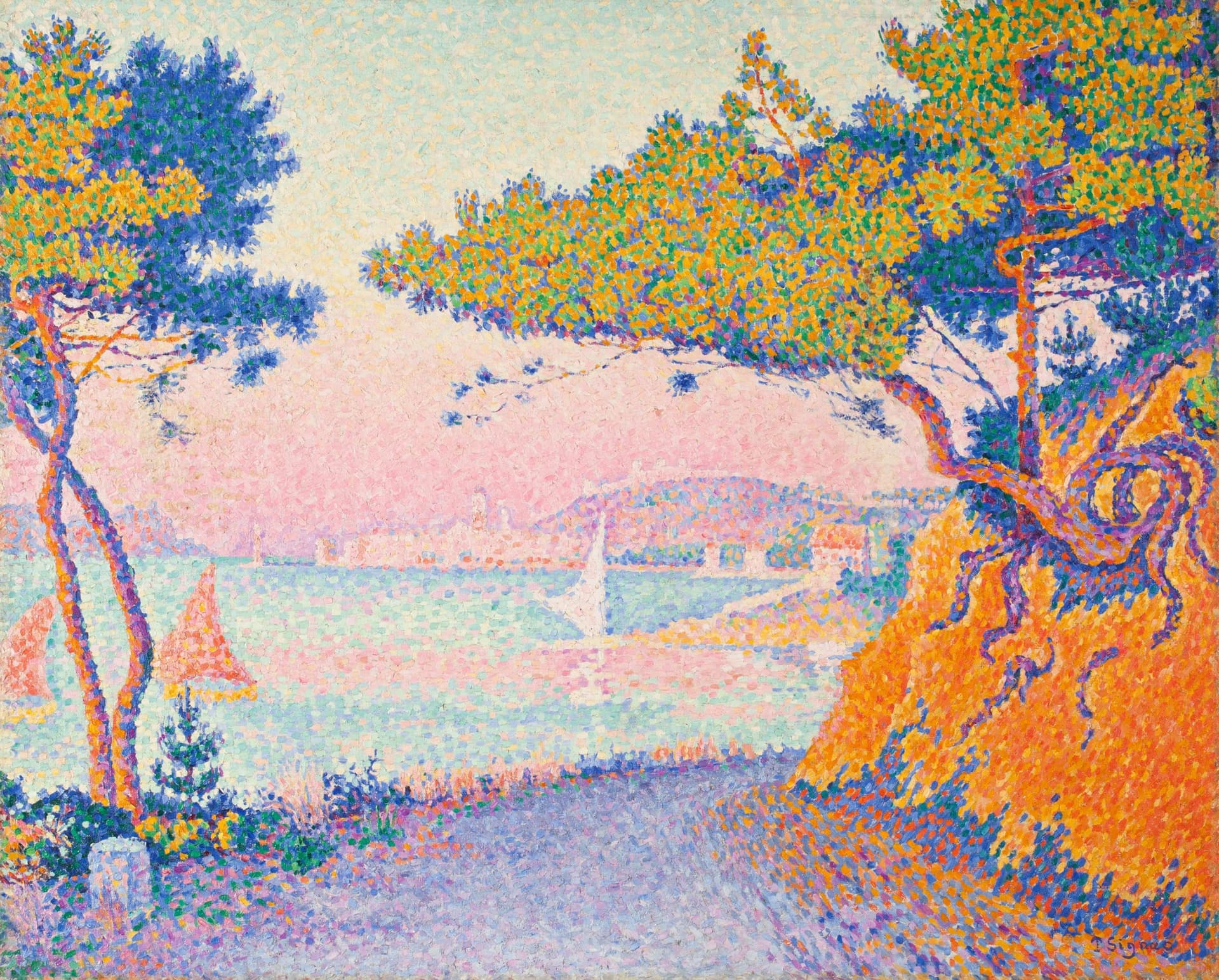
Neo-Impressionism emerged from Impressionism but with a distinct approach. Georges Seurat, the father of Neo-Impressionism, developed the technique of Pointillism, applying small dots of color to create a mosaic-like effect. His work, such as "A Sunday Afternoon on the Island of La Grande Jatte," is a cornerstone of the movement.
Read more about Neo-Impressionism.
Neoclassicism
This art style is characterized by idealized forms, balance, and order inspired by ancient Greek and Roman art. Its purpose is to create harmonious compositions that reflect the ideals of reason and logic. The word "Neoclassicism" translates to "New Classicism," reflecting the movement's revival of classical styles.
The rise of Neoclassicism was influenced by The Enlightenment, Archaeological Discoveries, writings of Johann Winckelmann, and artists like Jacques-Louis David. The Oath of the Horatii by Jacques-Louis David, Death of Marat by Jacques-Louis David, and The Birth of Venus by William-Adolphe Bouguereau are famous neo-classic paintings.
Read more about Neoclassicism.
Neon Art

The key factors in its emergence were the invention of neon lighting by Georges Claude, Art Deco, European Dada, Futurism, and Gaslight Era Signage. Work by renowned artists entails Walking Spirit by Bruce Nauman, The Running Man by Tracey Emin, and Viva Las Vegas by Claes Oldenburg.
Read more about Neon art.
Op Art
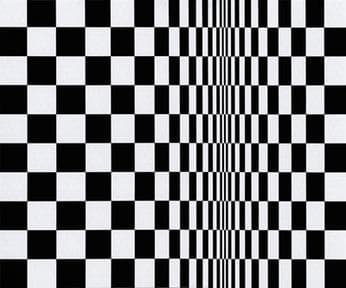
The rise of Op Art in the mid-20th century was due to movements and ideas like Constructivism, Bauhaus, Kinetic Art, and Gestalt Psychology. If you want to look at Op Art, try Current (1964), Vega (1964), Zebra (1938), etc.
Read more about Op Art.
Performance Art

The Fluxus movement, Dada, Futurism, Expressionism, and Body Art influenced the start of Performance art. These movements, along with individual artists' experimentation, created a fertile ground for Performance Art to emerge. Marina Abramović, Vito Acconci, and Tehching Hsieh are popular performance artists.
Read more about Performance Art.
Photorealism

This art style emerged because of Pop Art's focus on blurring the lines between high and low culture and hyperrealism's focus on creating realistic sculptures. Freeway by Richard Estes, 57 Chevy by Ralph Goings, and Diner by Edward Hopper are famous photorealistic artworks.
Read more about Photorealism.
Pop Art

Pop Art challenges traditional fine art by incorporating imagery from popular culture, advertising, and mass media. It involves bold colors, recognizable characters, and everyday objects to create works that reflect energy and consumerism of an era.
The Pop art movement emerged in the mid-1950s. The Dada anti-establishment movement paved the way for Pop Art as well as the rise of consumerism and mass media in post-war American society.
Some famous pop artworks are Campbell's Soup Cans (1962), Whaam! (1963), My Marilyn (1967), and I Love Lucy (1965).
Read more about Pop Art.
Portraiture

Early forms of portraiture can be traced back to ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia, and Greece. They created sculptures depicting pharaohs, rulers, and gods. Mona Lisa is the most famous Portraiture to exist.
Read more about Portraiture.
Post-Impressionism

Post-Impressionism began as a reaction to Impressionism. While Impressionists focused on capturing the effects of light and atmosphere, Post-Impressionists explored more personal expression, symbolism, and emotional content.
The term "Post-Impressionism" literally describes its position in art history. The word "Post" means "coming after" in Latin and Impressionism is the movement it stemmed from.
Post-Impressionism was also influenced by Individual Expression, Symbolism, Japanese Woodblock Prints, as well as Non-Western art styles.
If you want to see post-impressionism, The Starry Night by Vincent van Gogh and Sunflowers by him are the best examples.
Read more about Post-Impressionism.
Precisionism
Precisionism started in the 20th century in the United States. It represents objects and scenes with a focus on clarity, geometric forms, and mechanical precision. Precisionism incorporates elements of Cubism and Futurism but with a more realistic and industrial aesthetic.
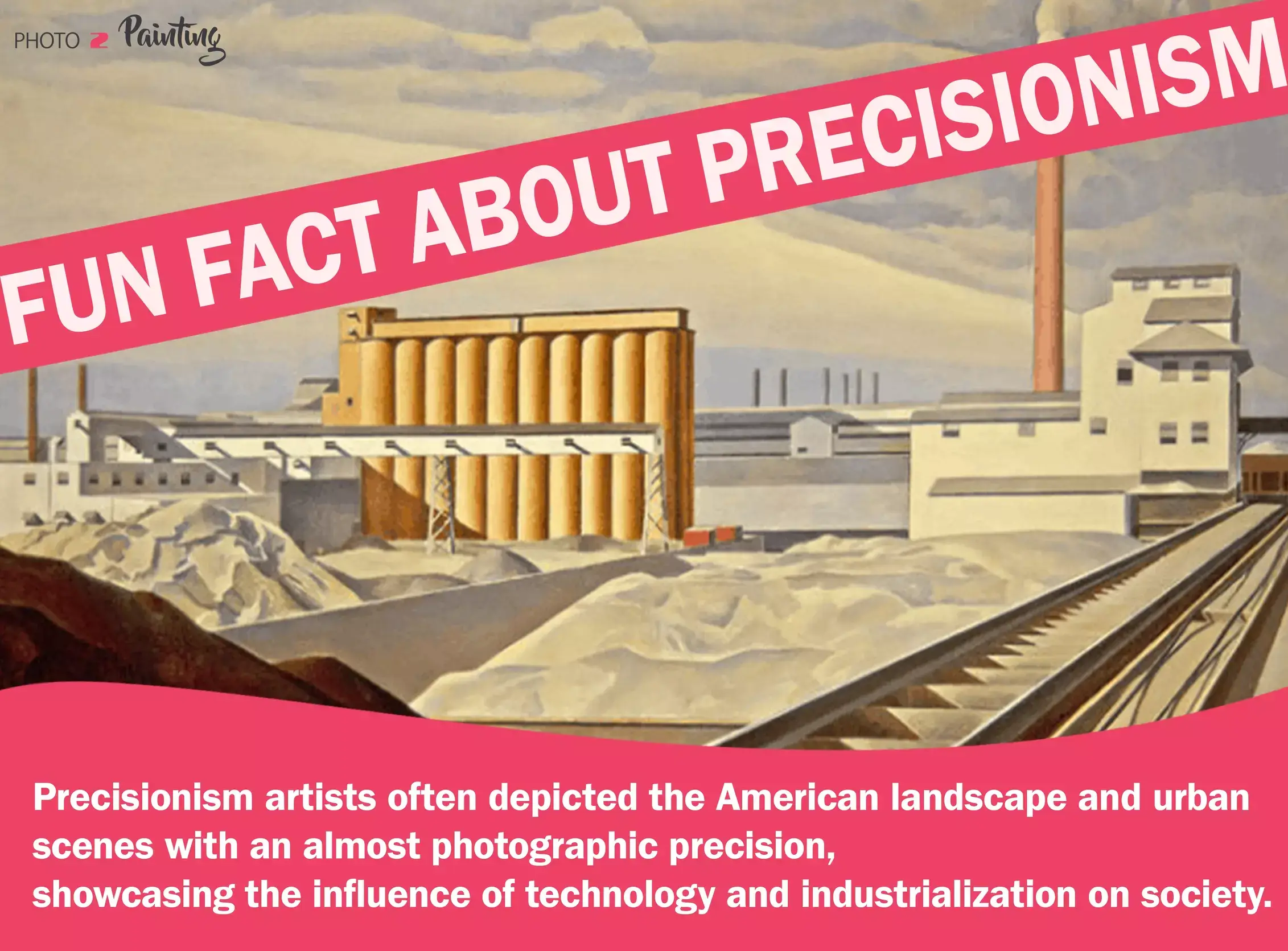
The word "Precisionism" reflects the emphasis on machine-like rendering of forms. Charles Sheeler and Morton Livingston are considered pioneers of Precisionism. Their shared interest in industrial subjects and meticulous rendering defined Precisionism's characteristics. Charles Sheeler's paintings like American Landscape, Elevator, and Precision Still Life are the best representations of this art style.
Read more about Precisionism.
Rococo

Rococo embraced ornamentation, playful themes, and asymmetry. It emphasized lightness, movement, and a carefree spirit, often depicting scenes of love, leisure, and mythology in a charming and decorative style.
The word "Rococo" was derived from Rocaille, the French term for rockwork or shellwork.
The artistic movement flourished under the patronage of King Louis XV. The focus on leisure, pleasure, and lighthearted themes reflected the desires of the court.
Some popular Rococo artworks were The Swing by Jean-Honoré Fragonard, The Toilet of Venus by François Boucher, and Pierrot by Jean-Antoine Watteau.
Read more about Rococo.
Romanticism
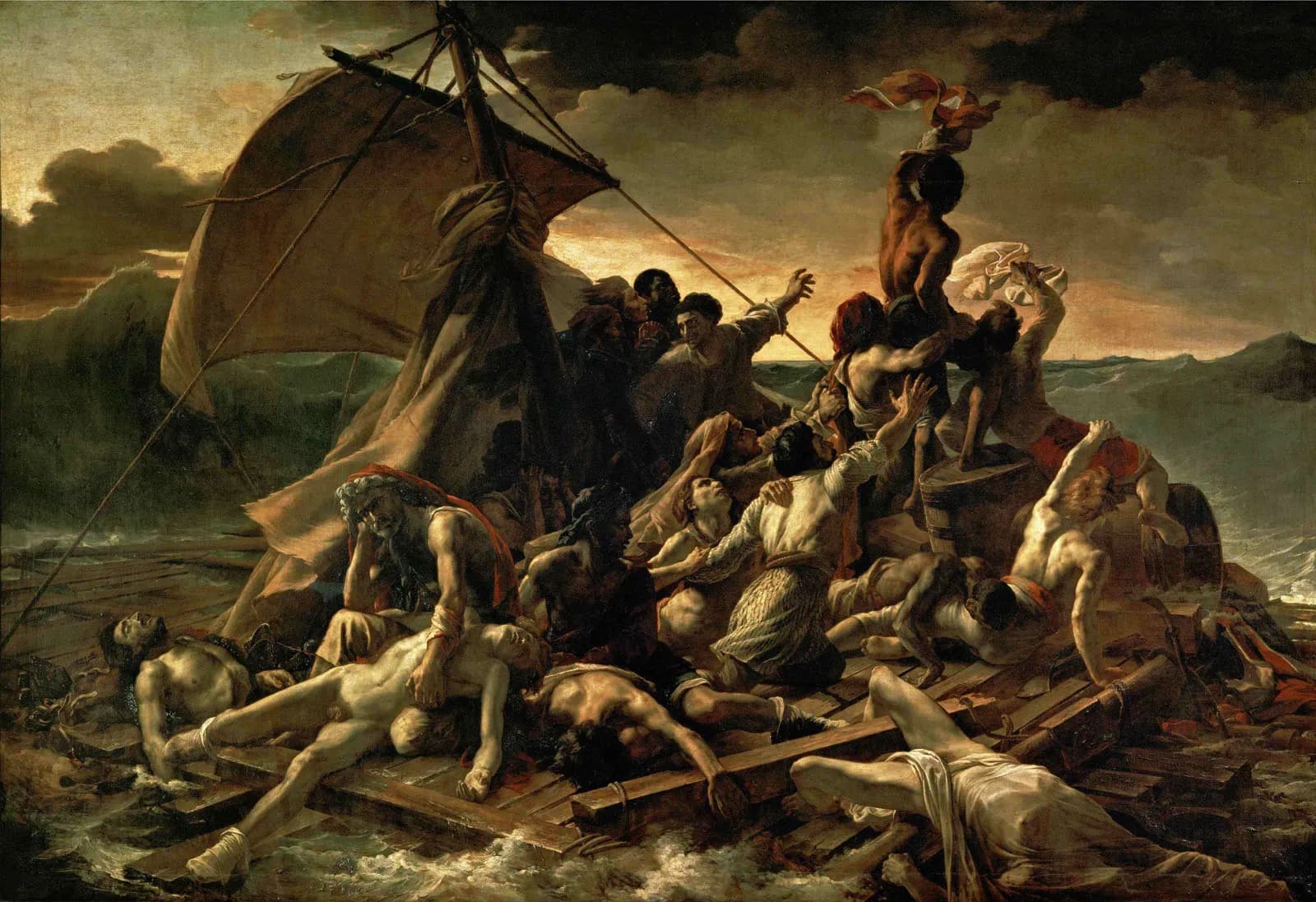

Romanticism relates to interest in emotions, imagination, and themes similar to those found in medieval romances, such as tales of chivalry and adventure. The 18th-century German movement 'German Sturm und Drang' is considered a precursor to Romanticism. It focused on individualism and emotional expression.
Liberty Leading the People, The Raft of the Medusa, and Wanderer above the Sea of Fog are the best examples of Romanticism.
Read more about Romanticism.
Spiritual Art
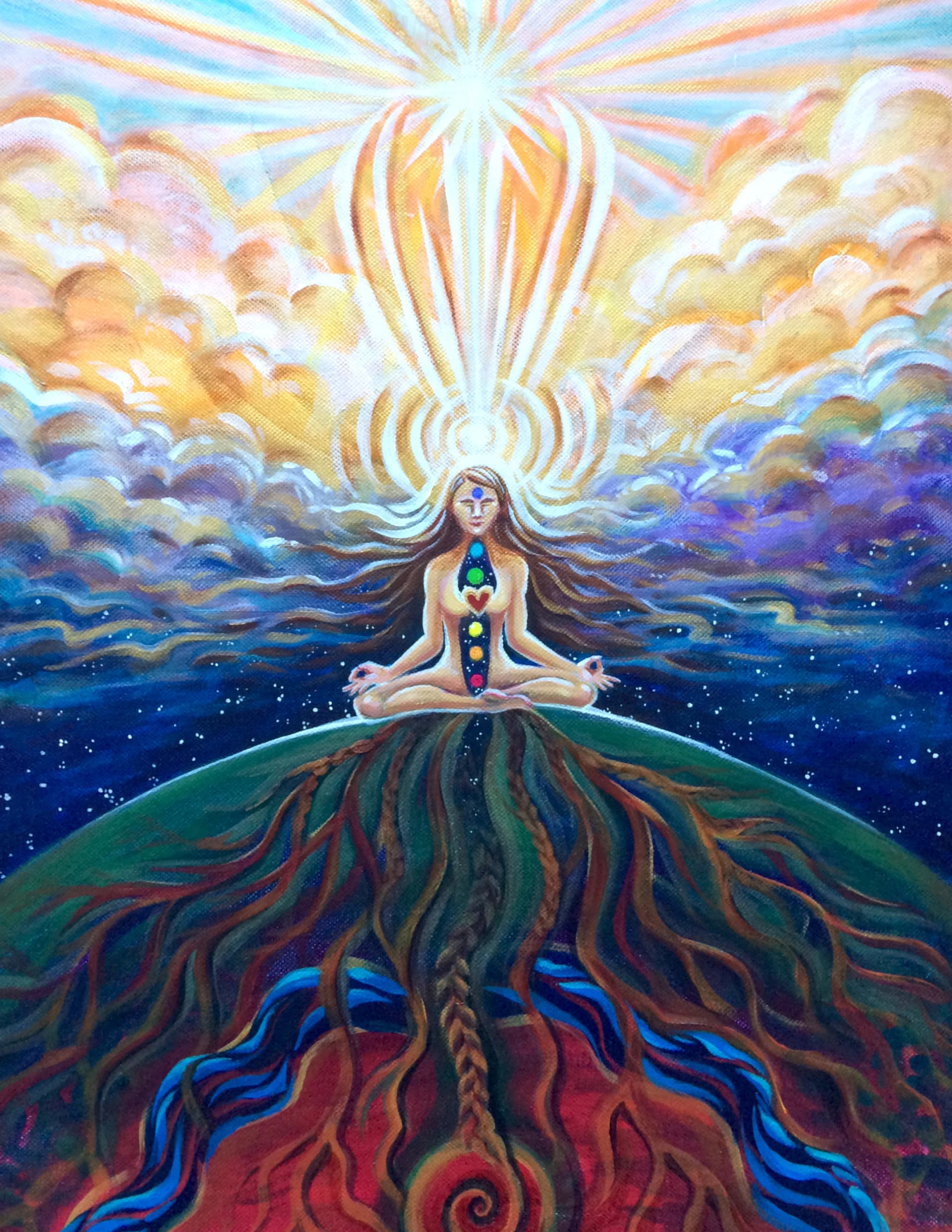

Spiritual art encompasses a wide range of artistic expressions that explore themes of the human spirit, religion, and transcendence.
It often uses symbolism, allegory, and religious iconography to evoke a sense of the divine or a connection to a higher power.
You can find Spiritual Art in various cultures and religions throughout history, serving as a powerful tool for meditation, devotion, and spiritual contemplation.
For example, in Western Religious Art, there are paintings like Sistine Madonna and The Creation of Adam. In Eastern Religious Art, there's Taj Mahal, Bhaisajyaguru Buddha, and Chidambaram Nataraja.
Read more about Spiritual art.
Street Art

Modern Street Art has its roots in the latter half of the 20th century. It started in the 1960s and early 1970s in major cities like New York and Philadelphia, such as Blek le Rat: Stenciled Rats and Mr. Brainwash: Life is Beautiful.
Read more about Street Art.
Surrealism

Giorgio de Chirico's dreamlike landscapes and unsettling juxtapositions are considered a precursor to Surrealism. He influenced Salvador Dalí, as seen in his works: The Persistence of Memory, The Lobster Telephone, and The Persistence of Myth (1952) by Salvador Dalí.
Read more about Surrealism.
Suprematism
Suprematism started in the early 20th century in Russia. It covers geometric abstraction in art. You can see basic geometric shapes like squares, circles, and lines and contrasting colors creating dynamism and non-objectivity in this art style.

The word "Supremus" means "highest" or "ultimate" in Latin, therefore, signifying the use of basic geometric shapes as the foundation of art in Suprematism. It was developed by Kazimir Malevich, who was interested in Russian folk art. You can see the influence of Russian folk art in his work, including Black Square (1915), White on White (1918), and Red Square (1915).
Read more about Suprematism.
Symbolism
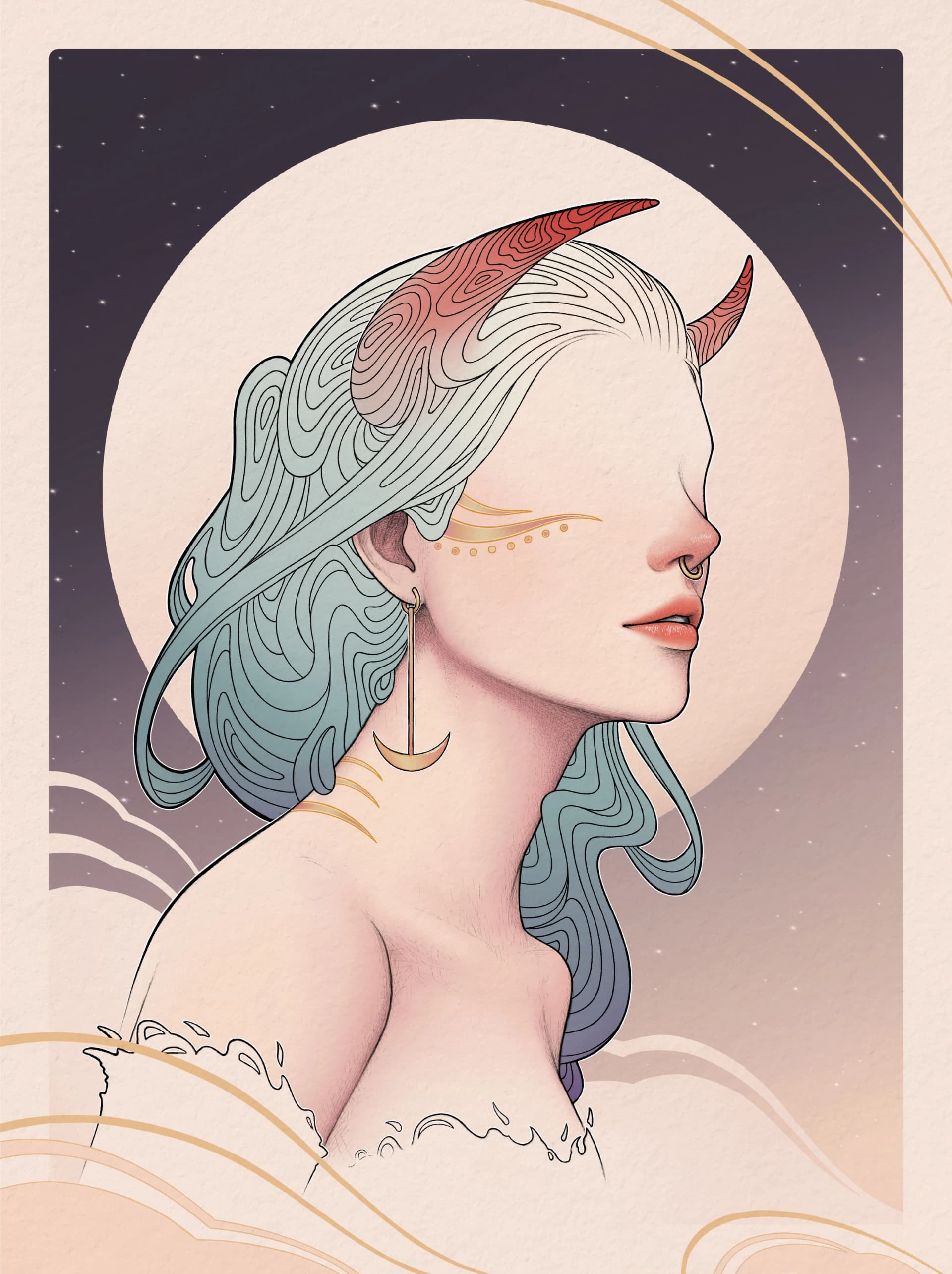

Symbolism is all about objects, figures, and colors conveying symbolic meanings beyond their literal depiction. It evokes emotions and ideas through allegory, metaphor, and dreamlike imagery.
It also explores themes of spirituality, the subconscious, and the beauty of the ideal.
The word "Symbolism" gained recognition around 1886 with the publication of a Symbolist manifesto.
Charles Baudelaire heavily influenced the beginning of Symbolism. His collection "Les Fleurs du Mal" addressed dark themes, explored the subconscious, and used symbolism heavily.
The Scream by Edvard Munch and The Kiss by Gustav Klimt are the most sought-after symbolic artworks.
Read more about Symbolism.
Zero Group
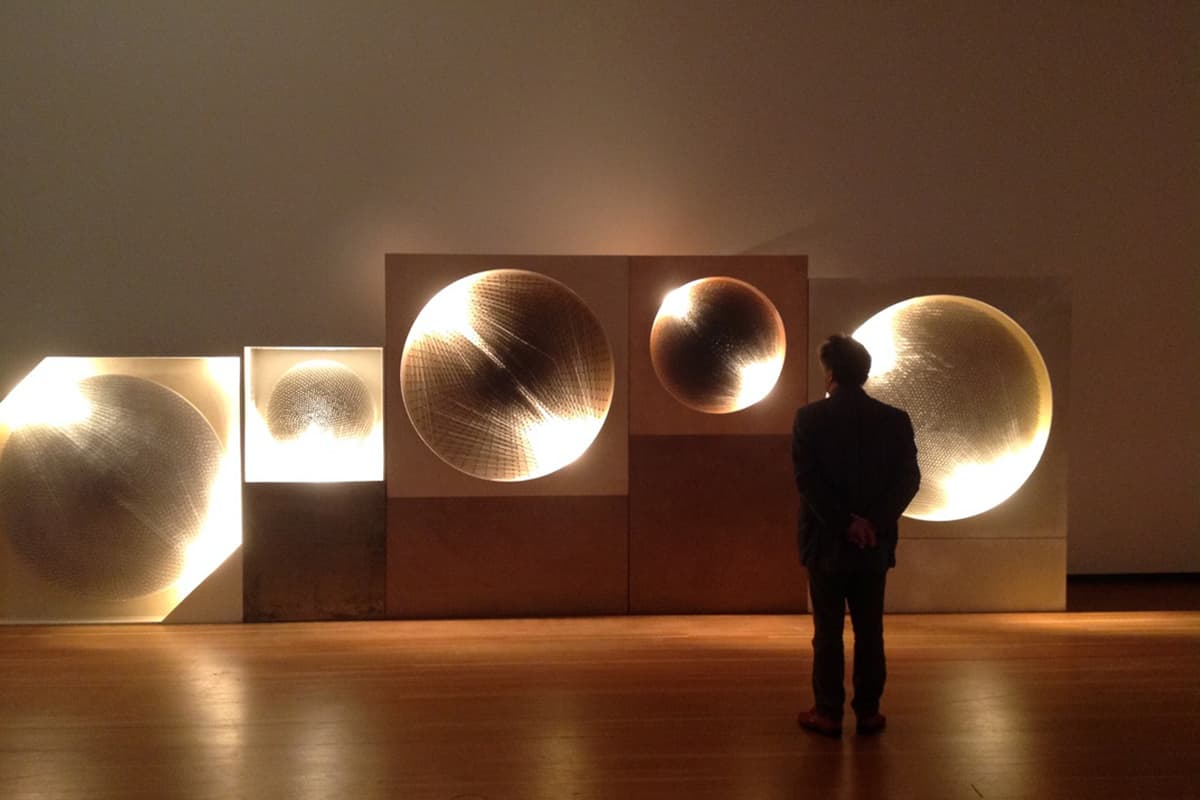

The word "Zero" signifies a fresh beginning, a tabula rasa, showing the movement's focus on pure experience and eliminating preconceptions in art. Zero emerged alongside other movements like Art Informel and Tachisme following the devastation of World War II.
Chromoplastics by Heinz Mack and Vibrationi Blu by Lucio Fontana are popular Zero Group artworks.
Read more about Zero Group
What is an Art Style?
An art style is the way a piece of art appears to you. The style is the way which an artist uses to depict his or her vision as well as the subject(s) in the artwork.
Art styles are determined by different aspects of an art movement. For example, the way an artist uses color, shadows, highlights, composition, and form is one way of defining an artwork. Factors that play a role in the evolution of art styles range from reaction to existing styles, cultural factors, and historical context to technological advancements and individual artistic exploration.
Some famous artist styles you should know of include Renaissance, Baroque, Neoclassicism, Cubism, Ukiyo-e, and Shan Shui.
How Many styles of art are there?
More than 75 types of art painting styles exist in the world of art today. Some prominent art styles among those 75 artistic movements include Land art, Kinetic art, Light and Space art, Biomorphism as well as Op Art.
What are the examples of 19th century art styles?
The examples of 19th century art styles include Romanticism, Realism, Symbolism, Neoclassicism, Impressionism, Art Nouveau, and Post-Impressionism.
What are the examples of 1940s art style?
The examples of 1940s art style include Abstract Expressionism, Color Field Painting, Post-Painterly and Hard-Edge Abstraction.
What are the examples of 1950s art style?
The examples of 1950s art style include Abstract Expressionism. However, it influenced many art practices worldwide, like Modern sculpture, Pop Art, Neo-dada, Art Informel, and Lyrical Abstraction.
What are examples of 1960's art style?
The examples of 1960's art style include art movements like Pop Art, Op Art, Minimalism, Conceptual Art, Performance Art, and Feminist Art.
What are the examples of cool art styles?
If you are looking for examples of cool art styles, you need to search for Surrealism, Pop Art, Street Art, Lowbrow Art, Neon Art, Op Art.
What are the examples of unique art styles?
The examples of Unique art styles include Anamorphic Art, Kinetic Art, Land Art, Light and Space Movement, Outsider Art, Bio Art among many more.
What are the examples of easy art styles?
The examples of easy art styles include artistic movements such as Minimalism, Cartoon, or Abstract Art. They are often considered more approachable for beginners.
What are the examples of simple cute art styles?
Examples of simple cute art styles include Chibis, Kawaii, Doodle Art, Emoji Art, Pixel Art, Flat Design, Sticker Style, and many more.
What are the examples of old art styles?
Examples of old art styles are Renaissance Art, Baroque, Neoclassicism, Realism, and Fauvism.
What are the examples of classical art styles?
Examples of classical art styles entail art movements such as Classicism Art, Ancient Greek Art, Roman Art, and Neoclassicism.
What are the examples of historical art styles?
Historical art styles are rich in history. Some of their examples include Renaissance Art, Baroque, Neoclassicism, Realism, and Impressionism.
What are the examples of colorful art styles?
Examples of colorful art styles are Pop Art and Surrealism.
What are the examples of drawing styles?
Examples of drawing styles include Caricature drawing, Cartoon drawing, Figure drawing, and Gesture drawing.
What are the examples of aesthetic art styles?
Examples of aesthetic art styles are Impressionism, Cubism, and Abstract Expressionism.
What are the types of painting styles?
The types of painting styles include Realism, Photorealism, Expressionism, Impressionism, Abstract, and Surrealism.
What are the examples of popular painting styles?
The examples of popular painting styles include Abstract, Modern, Pop Art, Cubism, Surrealism, Contemporary, and Fantasy.
What is an Artistic Movement?
An artistic movement is a trend or style in art with a shared philosophy and set of characteristics. It emerges during a specific period, often as a reaction to previous styles, and defines a generation of artists.
Some examples of artistic movements are Renaissance, Impressionism, and Pop Art.
What are the art movements of the 19th century?
The examples of art movements of the 19th century include Romanticism, Realism, Impressionism, Symbolism, Neoclassicism, Post-Impressionism, and Art Nouveau.
What are the examples of 20th century art movements?
The examples of art movements of the 20th century include Fauvism, Cubism, Futurism, Dada, Surrealism, Abstract Expressionism, Pop Art, Minimalism, Conceptual Art, Photorealism, and Neo-Expressionism.
What are examples of the American art movement?
The examples of American art by famous American artists include Abstract Expressionism, Action Painting, American Realism, American Regionalism.
What is an example of the nature art movement?
An example of nature art is Naturalism. Naturalism (19th century) depicted life realistically, focusing on everyday scenes, social issues, and the working class, often with a focus on scientific observation.
What are the examples of current artistic movements?
Examples of current artistic movements include Minimalism, Conceptual Art, Fluxus, and Photorealism.
What is an art period?
An art period is a broad time frame in art history encompassing various artistic movements that share stylistic elements and historical context. These periods can last centuries and encompass artistic evolution.
Some examples of the art period include Renaissance, the Baroque era, and the Romantic period.
What are the types of fine arts?
The types of fine arts include Visual Arts, Performing Arts, Literary Arts, and Architecture.
What are the different types of artists?
The different types of artists include Visual Artists, Performing Artists, Literary Artists, Media Artists, and Digital Artists. Famous artists include Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo, Vincent van Gogh, Claude Monet, and Pablo Picasso.
What are the different types of art schools?
The different types of art schools include Fine Arts Schools, Animation Schools, Media Arts Schools, Performing Arts Schools, Digital Arts Schools, and Craft Schools.
What are the names of the most common methodologies of art?
The most common methodologies of art are Formalism, Iconography, Marxism, Feminism, Biography, Psychoanalysis, Historical Context, and Semiotics.
What are the various forms of art?
The various forms of art include Visual Arts, Performing Arts, Architecture, Craft Arts, and Media Arts.
George, CEO of Photo2painting, is a passionate art lover and entrepreneur. He founded Photo2painting.com from scratch, inspired by his artist friends. As the company's CMO, he manages content and marketing.
Excellent Customer Reviews